
EXPLORE
The Cardano Ecosystem
....one click at a time.

The Cardano Ecosystem
....one click at a time.

Cardano is an open-source, permissionless blockchain network based on Proof-of- Stake (PoS) built on the work of over 120 academic papers. The heart and soul of the the project is the Cardano base layer blockchain. More generally, the project aims to build a sustainable, community-governed, decentralised ecosystem anchored by a borderless and trustless settlement layer for peer-to-peer payments and digital contracts. Derivative innovation on top of this ecosystem is anticipated to seamlessly adapt and provide new functionality over time and scale to support global adoption.
Central to Cardano’s mission, the project aims to empower and bring digital and financial identity to the estimated 2 billion to 3 billion people in the world that don’t currently have it, with an initial focus on Africa. Cardano’s lead development arm, IOG, is already working with government organisations in three different countries.
With ambitious goals, Cardano recognizes the necessity for their infrastructure to run correctly the first time it runs. This is in contrast to a “launch now, fix as we go” philosophy employed by many Silicon Valley development teams. Therefore, Cardano fosters a culture based on academic peer-review and formal verification, emphasising security, reliability, and sustainability around their finished product. While these characteristics are intuitively desirable, this approach comes at the cost of slower development rollout.
Cardano was created in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson and Jeremy Wood, both of whom are also considered co-founders of Ethereum. The project’s development is driven through the collaboration of three founding organisations, each of which have their own specific role:
Input Output Global (IOG or IOHK)—a for-profit blockchain research and engineering company founded by Hoskinson and Wood, which leads the research, development, and engineering of the Cardano blockchain.
EMURGO—a for-profit global blockchain solutions provider that focuses on the promotion of Cardano-based commercial applications.
Cardano Foundation—an independent, Swiss-based non-profit which oversees and supervises the development of the Cardano blockchain.
The separation of roles and powers, particularly for-profit from non-profit organisations, is a common approach taken by many blockchain projects and open-source software projects, separating business interests from the development of community-owned, public infrastructure. In particular, the separation between the non-profit Cardano Foundation and the original development team is another demonstration of the project’s commitment to community ownership and governance.
Cardano is considered to be a 3rd-generation blockchain, which are blockchain networks designed to provide smart contract functionality with an emphasis on scalability, interoperability, and sustainability. These blockchains attempt to address commonly held views on the limitations of networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are considered 1stgeneration and 2nd-generation blockchains, respectively.
Scalability—ability of a blockchain to support a growing number of users and devices. With global adoption in mind, for most of these projects that means users in the billions. Common measures of scalability are throughput (i.e. transactions per second or TPS) and latency (i.e. the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed).
Interoperability—ability of a blockchain to interact with other blockchains and external resources such as APIs, whether that is to share state or information between two platforms or to trigger execution/computation on each other’s platforms.
Sustainability—this comes in two forms: environmental sustainability referring to the protocol’s ability to operate with low energy consumption and protocol/ ecosystem sustainability through the use of on-chain governance and a community treasury or funding resource.
Third-generation blockchains include a family of projects such as Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Polkadot, and Solana. These projects are often branded in Twitter circles as “Ethereum killers” as they are considered a threat to Ethereum’s reign in the smart contract platform sector. However, efforts to engineer interoperability suggest these projects strive to coexist alongside Ethereum, as well as one another, resulting in a multi-chain, decentralised Web3 ecosystem. Ironically, despite the “Ethereum Killer” label, Cardano is actually far more reminiscent of Bitcoin, particularly with respect to its tokenomics, consensus protocol, and accounting style.
To get a detailed market intelligence report to your email covering Cardano’s Tokenomics, Roadmap, Technology, Web3 Ecosystem as well as Network & Adoption, please send us this message:
“Cardano Market Report”

Stake with us and help truly decentralise the cardano ecosystem.
Once you have acquired your ADA it’s time to delegate it. Why delegate your ADA? That’s how you increase your amount of ADA without buying more. This is the basic principle of Proof of Stake. The steps are pretty straightforward
For this guide, we’re going to use Daedalus. If you have questions about how to delegate using different wallets, reach out directly to us and we’d be happy to help.
STEP 1 : CLICK ON THE NETWORK TAB
Specifically, open up your Daedalus, Mainnet wallet. Then, wait for it to fully sync and click on the network tab on the left.
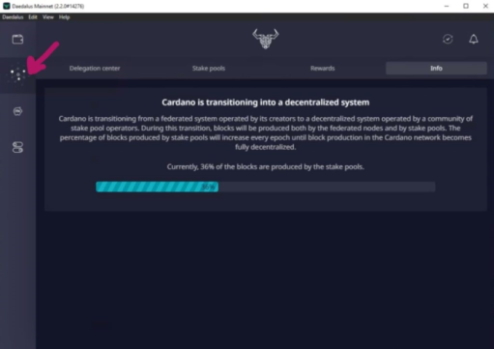
STEP 2: CLICK ON THE STAKE POOLS TAB
This is the built-in stake pool browser within Daedalus. You will see a list of all available stake pools. Search for the ticker for the pool that you would like to delegate to (like MASAI).
STEP 3: DELEGATE YOUR WALLET
Click on the tile for the pool that you’d like to delegate to. Then click on “Delegate to this pool”. You will be asked to select the wallet that you’d like to delegate. Select your wallet and confirm.
That’s it! You’re done! Prepare to receive your rewards two epochs from now.
Please note that this process will change slightly when IOHK introduces portfolios and the ability to delegate partial wallets.


This is bold and this is strong. This is italic and this is emphasized.
This is superscript text and this is subscript text.
This is underlined and this is code: for (;;) { ... }. Finally, this is a link.
Fringilla nisl. Donec accumsan interdum nisi, quis tincidunt felis sagittis eget tempus euismod. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus vestibulum. Blandit adipiscing eu felis iaculis volutpat ac adipiscing accumsan faucibus. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus lorem ipsum dolor sit amet nullam adipiscing eu felis.
i = 0;
while (!deck.isInOrder()) {
print 'Iteration ' + i;
deck.shuffle();
i++;
}
print 'It took ' + i + ' iterations to sort the deck.';| Name | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Item One | Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. | 29.99 |
| Item Two | Vis ac commodo adipiscing arcu aliquet. | 19.99 |
| Item Three | Morbi faucibus arcu accumsan lorem. | 29.99 |
| Item Four | Vitae integer tempus condimentum. | 19.99 |
| Item Five | Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. | 29.99 |
| 100.00 | ||
| Name | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Item One | Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. | 29.99 |
| Item Two | Vis ac commodo adipiscing arcu aliquet. | 19.99 |
| Item Three | Morbi faucibus arcu accumsan lorem. | 29.99 |
| Item Four | Vitae integer tempus condimentum. | 19.99 |
| Item Five | Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. | 29.99 |
| 100.00 | ||